Susanne Köllmer, Dipl. Biol.

WP6: High-throughput knock-out screening for pathogenicity factors and developmental regulators in
B. sorokiniana
In this work package (WP) a high throughput screen will be used to identify pathogenicity genes and developmental regulators of the cereal pathogen Bipolaris sorokiniana.
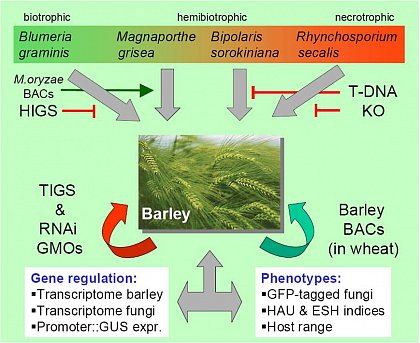
This work package aims at establishing a quantitative correlation between fungal gene function and disease phenotype in the interaction of the hemibiotrophic fungus B. sorokiniana and barley. To this end, the development of pathogenicity and virulence mutants of B. sorokiniana on barley will be compared to the compatible wild-type interaction. To identify fungal candidate genes two strategies will be followed: (1) random T-DNA insertion mutagenesis via Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated transformation (ATMT) of a GFP-tagged fungal strain and (2) identification of cDNAs encoding secreted proteins (“secretome”) using a bacterial signal sequence trap (SST), followed by targeted displacement of selected genes through homologous recombination. Gene identification will be facilitated by using the possibility of high-throughput SST/cDNA sequencing. Development of the ATMT- and SST-derived mutants will be quantitatively analysed using the automated pattern recognition tool HyphArea that has been successfully applied to the interaction of barley and Bgh and that will be adapted to the B. sorokiniana -barley situation.
This approach will allow addressing genes involved in different pathogenicity strategies, as the pathogens R. secalis and B. sorokiniana exhibit different lifestyles.
Of particular interest will be to visualize the three-dimensional pathogenic mycelium within the infected leaf. To complement the microscopical data, qPCR techniques will be used to quantify fungal development (WP5, WP7).
A yeast-based secretome screen (signal-sequence-trap) will allow identifying genes encoding proteins secreted at defined stages of the B. sorokiniana-barley interaction and deliver candidate pathogenicity or virulence genes. These genes can subsequently be characterized in a screen by targeted mutagenesis. Mutants exhibiting interesting phenotypes will be used to analyse the effect of the inactivated genes of the pathogen on host gene expression (cooperation with WP1, WP2, WP7, WP5). Gene expression in selected mutants will by analysed in the context of host-gene expression by using the dedicated interaction microarray (WP9). Finally, pathogenicity or virulence genes that are conserved across biotrophs, hemibiotrophs and necrotrophs can be used to test their feasibility for „host-induced gene silencing“ (HIGS) in transgenic barley or wheat plants (WP9 and WP10).
Bipolaris GABI

